Tomcat - Container的管道机制:责任链模式
Tomcat - Container的管道机制:责任链模式
提示
上文中介绍了Engine的设计,其中有Pipline相关内容没有介绍,本文将向你阐述Tomcat的管道机制以及它要解决的问题。
- Tomcat - Container的管道机制:责任链模式
- 内容引入
- 知识准备
- 责任链模式
- FilterChain
- Pipline机制
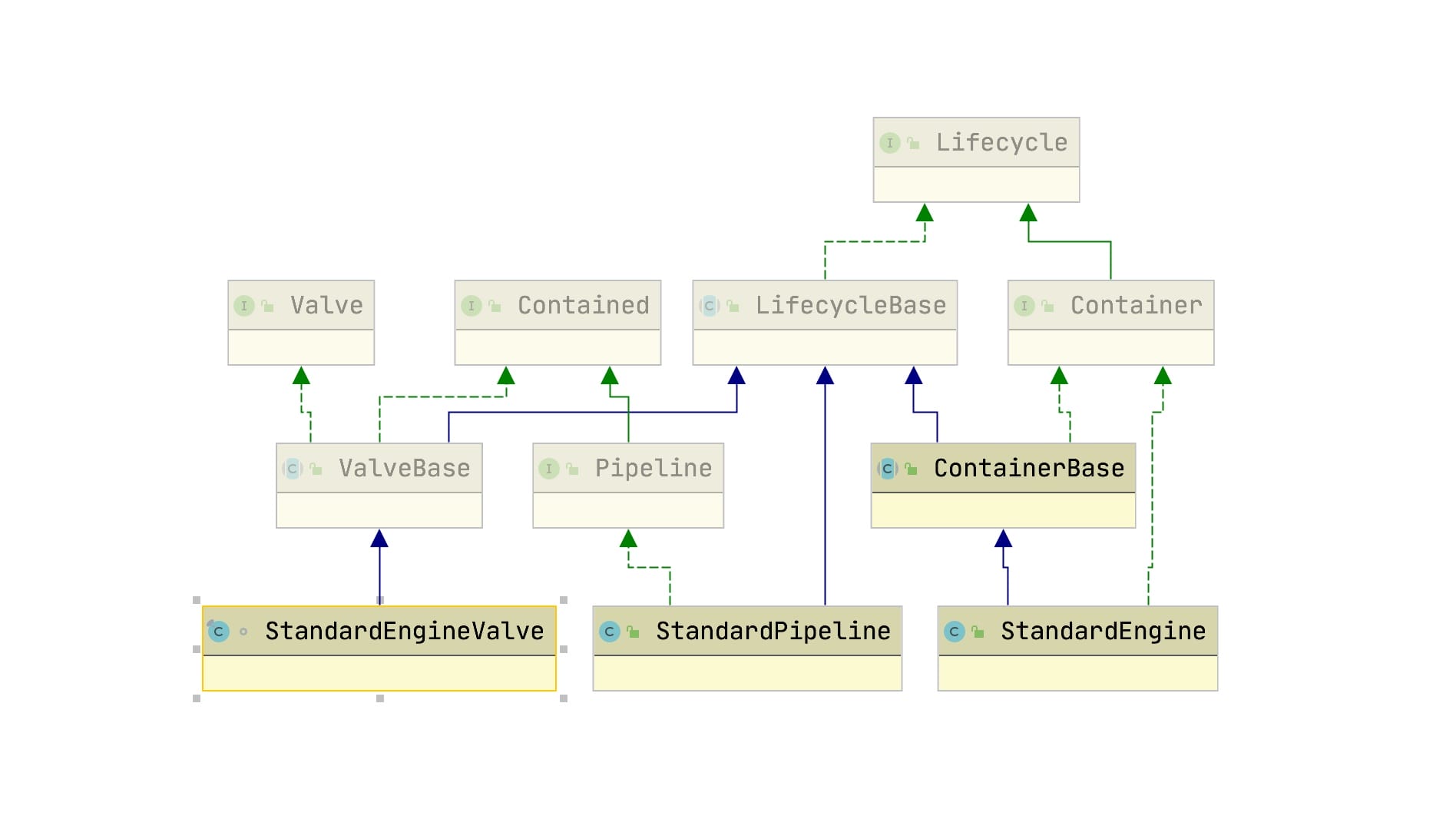
- Vavle接口设计
- Pipline接口设计
- BaseVavle设计
- StandardPipline实现
- ContainerBase中运用Pipline
- 对比下两种责任链模式
内容引入
承接上文Engine的设计,从以下几个方面,我将向你解释为什么要理解Tomcat中管道机制,它要解决什么问题?
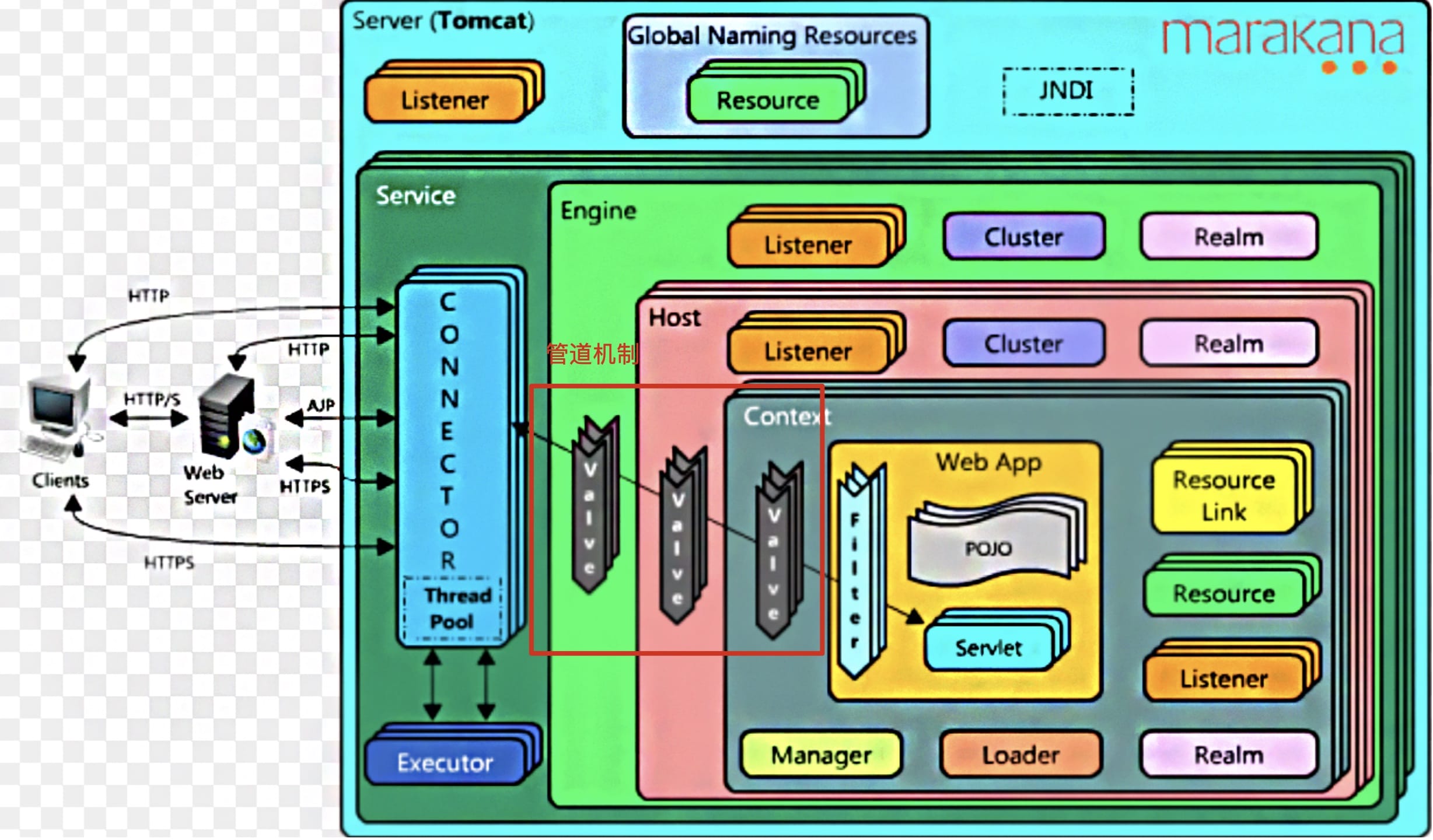
- 我们在上文Engine中有一块Pipline没有解释:
- 为什么Tomcat要引入Pipline呢?它要解决什么问题呢?
下文将向你详细阐述。
知识准备
在弄清楚管道机制前,你需要一些基础知识和其它软件设计中的应用场景。
责任链模式
管道机制在设计模式上属于责任链模式,如果你不理解,请参看如下文章:
责任链模式(Chain of responsibility pattern) : 通过责任链模式, 你可以为某个请求创建一个对象链. 每个对象依序检查此请求并对其进行处理或者将它传给链中的下一个对象。
FilterChain
在软件开发的常接触的责任链模式是FilterChain,它体现在很多软件设计中:
- 比如Spring Security框架中
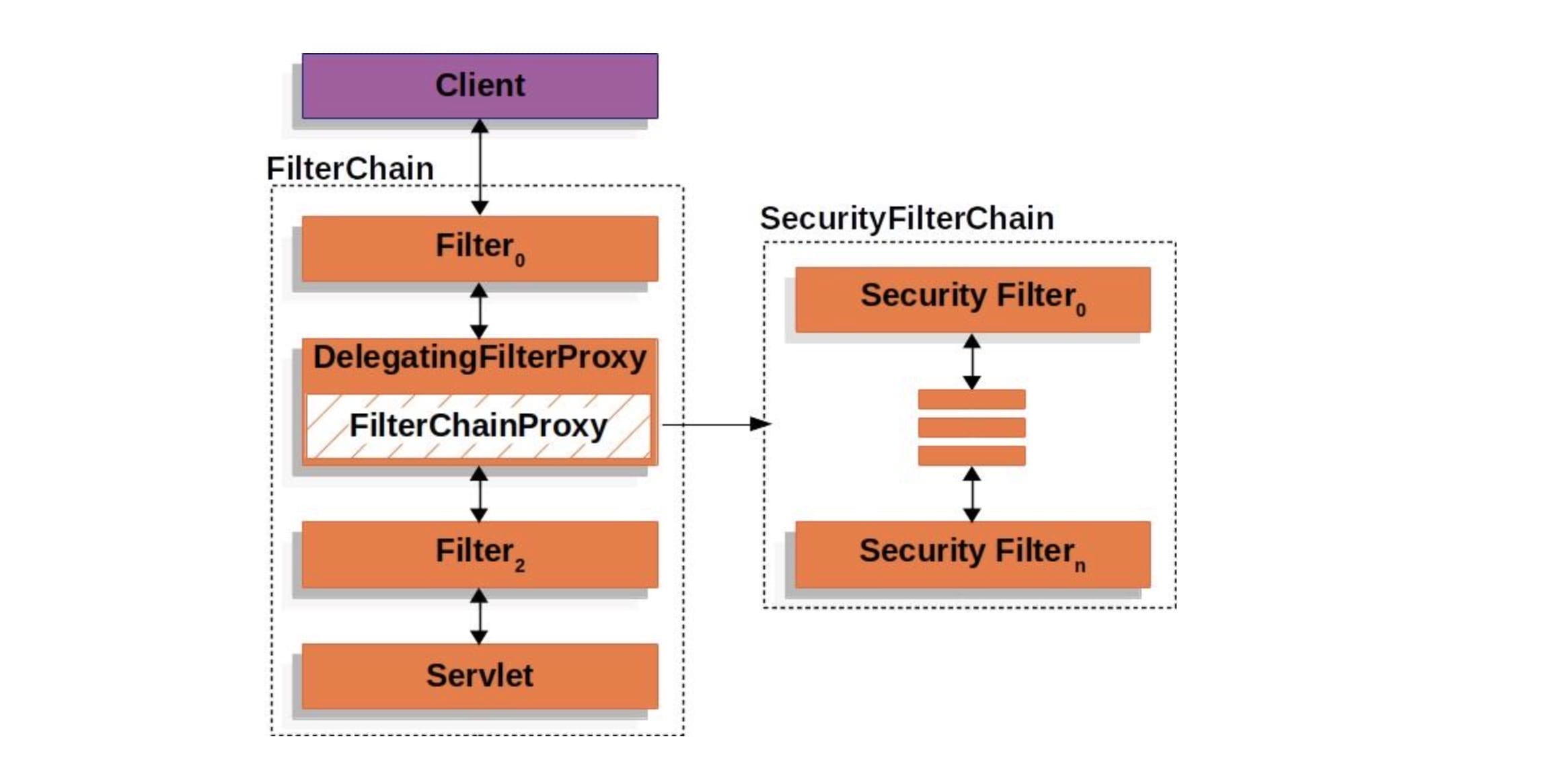
- 比如HttpServletRequest处理的过滤器中
当一个request过来的时候,需要对这个request做一系列的加工,使用责任链模式可以使每个加工组件化,减少耦合。也可以使用在当一个request过来的时候,需要找到合适的加工方式。当一个加工方式不适合这个request的时候,传递到下一个加工方法,该加工方式再尝试对request加工。
网上找了图,这里我们后文将通过Tomcat请求处理向你阐述。
Pipline机制
为什么要有管道机制?
在一个比较复杂的大型系统中,如果一个对象或数据流需要进行繁杂的逻辑处理,我们可以选择在一个大的组件中直接处理这些繁杂的业务逻辑,这个方式虽然达到目的,但扩展性和可重用性较差, 因为可能牵一发而动全身。更好的解决方案是采用管道机制, 用一条管道把多个对象(阀门部件)连接起来,整体看起来就像若干个阀门嵌套在管道中一样,而处理逻辑放在阀门上 。
Vavle接口设计
理解它的设计,第一步就是阀门设计
public interface Valve {
// 因为需要传递给下个Valve处理,所以有next
public Valve getNext();
public void setNext(Valve valve);
// 设计这个方法,便于执行周期任务,比如重新加载组件。此方法将在该容器的类加载上下文中调用。
public void backgroundProcess();
// 这个方法很容易理解,阀门中处理的执行方法,传入Request和Response进行处理
public void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException;
// 此阀门是否支持Servlet 3+ 异步的请求
public boolean isAsyncSupported();
}
Pipline接口设计
由于Pipline是为容器设计的,所以它在设计时加入了一个Containerd接口, 就是为了制定当前Pipline所属的容器:
public interface Contained {
Container getContainer();
void setContainer(Container container);
}
我们接着看下Pipline接口设计
public interface Pipeline extends Contained {
// 基础的处理阀
public Valve getBasic();
public void setBasic(Valve valve);
// 对节点(阀门)增删查
public void addValve(Valve valve);
public Valve[] getValves();
public void removeValve(Valve valve);
// 获取第一个节点,遍历的起点,所以需要有这方法
public Valve getFirst();
// 是否所有节点(阀门)都支持处理Servlet3异步处理
public boolean isAsyncSupported();
// 找到所有不支持Servlet3异步处理的阀门
public void findNonAsyncValves(Set<String> result);
}
BaseVavle设计
由于Valve也是组件,需要生命周期管理,所以实现LifecycleMBeanBase,同时集成Contained和Valve
public abstract class ValveBase extends LifecycleMBeanBase implements Contained, Valve {
protected static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(ValveBase.class);
//------------------------------------------------------ Constructor
public ValveBase() {
this(false);
}
public ValveBase(boolean asyncSupported) {
this.asyncSupported = asyncSupported;
}
//------------------------------------------------------ Instance Variables
/**
* Does this valve support Servlet 3+ async requests?
*/
protected boolean asyncSupported;
/**
* The Container whose pipeline this Valve is a component of.
*/
protected Container container = null;
/**
* Container log
*/
protected Log containerLog = null;
/**
* The next Valve in the pipeline this Valve is a component of.
*/
protected Valve next = null;
//-------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
/**
* Return the Container with which this Valve is associated, if any.
*/
@Override
public Container getContainer() {
return container;
}
/**
* Set the Container with which this Valve is associated, if any.
*
* @param container The new associated container
*/
@Override
public void setContainer(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return asyncSupported;
}
public void setAsyncSupported(boolean asyncSupported) {
this.asyncSupported = asyncSupported;
}
/**
* Return the next Valve in this pipeline, or <code>null</code> if this
* is the last Valve in the pipeline.
*/
@Override
public Valve getNext() {
return next;
}
/**
* Set the Valve that follows this one in the pipeline it is part of.
*
* @param valve The new next valve
*/
@Override
public void setNext(Valve valve) {
this.next = valve;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* Execute a periodic task, such as reloading, etc. This method will be
* invoked inside the classloading context of this container. Unexpected
* throwables will be caught and logged.
*/
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
// NOOP by default
}
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
containerLog = getContainer().getLogger();
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
/**
* Stop this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#stopInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
}
/**
* Return a String rendering of this object.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return ToStringUtil.toString(this);
}
// -------------------- JMX and Registration --------------------
@Override
public String getObjectNameKeyProperties() {
StringBuilder name = new StringBuilder("type=Valve");
Container container = getContainer();
name.append(container.getMBeanKeyProperties());
int seq = 0;
// Pipeline may not be present in unit testing
Pipeline p = container.getPipeline();
if (p != null) {
for (Valve valve : p.getValves()) {
// Skip null valves
if (valve == null) {
continue;
}
// Only compare valves in pipeline until we find this valve
if (valve == this) {
break;
}
if (valve.getClass() == this.getClass()) {
// Duplicate valve earlier in pipeline
// increment sequence number
seq ++;
}
}
}
if (seq > 0) {
name.append(",seq=");
name.append(seq);
}
String className = this.getClass().getName();
int period = className.lastIndexOf('.');
if (period >= 0) {
className = className.substring(period + 1);
}
name.append(",name=");
name.append(className);
return name.toString();
}
@Override
public String getDomainInternal() {
Container c = getContainer();
if (c == null) {
return null;
} else {
return c.getDomain();
}
}
}
StandardPipline实现
里面方法很简单,就直接贴代码了。它必然是继承LifecycleBase同时实现Pipline.
贴个图方面你理解
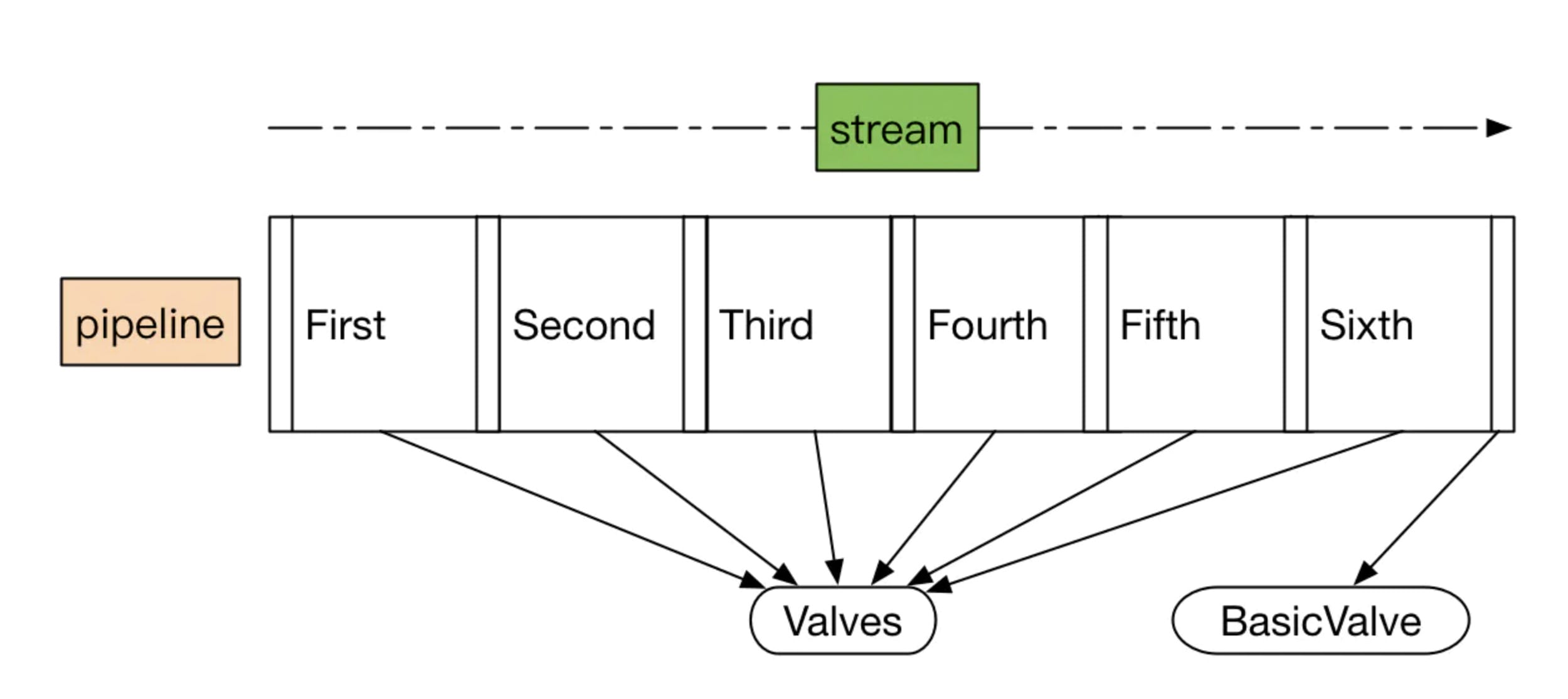
public class StandardPipeline extends LifecycleBase implements Pipeline {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(StandardPipeline.class);
private static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(Constants.Package);
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
/**
* Construct a new StandardPipeline instance with no associated Container.
*/
public StandardPipeline() {
this(null);
}
/**
* Construct a new StandardPipeline instance that is associated with the
* specified Container.
*
* @param container The container we should be associated with
*/
public StandardPipeline(Container container) {
super();
setContainer(container);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* The basic Valve (if any) associated with this Pipeline.
*/
protected Valve basic = null;
/**
* The Container with which this Pipeline is associated.
*/
protected Container container = null;
/**
* The first valve associated with this Pipeline.
*/
protected Valve first = null;
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
@Override
public boolean isAsyncSupported() {
Valve valve = (first!=null)?first:basic;
boolean supported = true;
while (supported && valve!=null) {
supported = supported & valve.isAsyncSupported();
valve = valve.getNext();
}
return supported;
}
@Override
public void findNonAsyncValves(Set<String> result) {
Valve valve = (first!=null) ? first : basic;
while (valve != null) {
if (!valve.isAsyncSupported()) {
result.add(valve.getClass().getName());
}
valve = valve.getNext();
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ Contained Methods
/**
* Return the Container with which this Pipeline is associated.
*/
@Override
public Container getContainer() {
return this.container;
}
/**
* Set the Container with which this Pipeline is associated.
*
* @param container The new associated container
*/
@Override
public void setContainer(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
@Override
protected void initInternal() {
// NOOP
}
/**
* Start {@link Valve}s) in this pipeline and implement the requirements
* of {@link LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).start();
current = current.getNext();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
/**
* Stop {@link Valve}s) in this pipeline and implement the requirements
* of {@link LifecycleBase#stopInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
// Stop the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).stop();
current = current.getNext();
}
}
@Override
protected void destroyInternal() {
Valve[] valves = getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
removeValve(valve);
}
}
/**
* Return a String representation of this component.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return ToStringUtil.toString(this);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------- Pipeline Methods
/**
* <p>Return the Valve instance that has been distinguished as the basic
* Valve for this Pipeline (if any).
*/
@Override
public Valve getBasic() {
return this.basic;
}
/**
* <p>Set the Valve instance that has been distinguished as the basic
* Valve for this Pipeline (if any). Prior to setting the basic Valve,
* the Valve's <code>setContainer()</code> will be called, if it
* implements <code>Contained</code>, with the owning Container as an
* argument. The method may throw an <code>IllegalArgumentException</code>
* if this Valve chooses not to be associated with this Container, or
* <code>IllegalStateException</code> if it is already associated with
* a different Container.</p>
*
* @param valve Valve to be distinguished as the basic Valve
*/
@Override
public void setBasic(Valve valve) {
// Change components if necessary
Valve oldBasic = this.basic;
if (oldBasic == valve)
return;
// Stop the old component if necessary
if (oldBasic != null) {
if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldBasic instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) oldBasic).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.basic.stop"), e);
}
}
if (oldBasic instanceof Contained) {
try {
((Contained) oldBasic).setContainer(null);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
}
}
// Start the new component if necessary
if (valve == null)
return;
if (valve instanceof Contained) {
((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container);
}
if (getState().isAvailable() && valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.basic.start"), e);
return;
}
}
// Update the pipeline
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == oldBasic) {
current.setNext(valve);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
this.basic = valve;
}
/**
* <p>Add a new Valve to the end of the pipeline associated with this
* Container. Prior to adding the Valve, the Valve's
* <code>setContainer()</code> method will be called, if it implements
* <code>Contained</code>, with the owning Container as an argument.
* The method may throw an
* <code>IllegalArgumentException</code> if this Valve chooses not to
* be associated with this Container, or <code>IllegalStateException</code>
* if it is already associated with a different Container.</p>
*
* @param valve Valve to be added
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if this Container refused to
* accept the specified Valve
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the specified Valve refuses to be
* associated with this Container
* @exception IllegalStateException if the specified Valve is already
* associated with a different Container
*/
@Override
public void addValve(Valve valve) {
// Validate that we can add this Valve
if (valve instanceof Contained)
((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container);
// Start the new component if necessary
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.valve.start"), e);
}
}
}
// Add this Valve to the set associated with this Pipeline
if (first == null) {
first = valve;
valve.setNext(basic);
} else {
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == basic) {
current.setNext(valve);
valve.setNext(basic);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
}
container.fireContainerEvent(Container.ADD_VALVE_EVENT, valve);
}
/**
* Return the set of Valves in the pipeline associated with this
* Container, including the basic Valve (if any). If there are no
* such Valves, a zero-length array is returned.
*/
@Override
public Valve[] getValves() {
List<Valve> valveList = new ArrayList<>();
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
valveList.add(current);
current = current.getNext();
}
return valveList.toArray(new Valve[0]);
}
public ObjectName[] getValveObjectNames() {
List<ObjectName> valveList = new ArrayList<>();
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current instanceof JmxEnabled) {
valveList.add(((JmxEnabled) current).getObjectName());
}
current = current.getNext();
}
return valveList.toArray(new ObjectName[0]);
}
/**
* Remove the specified Valve from the pipeline associated with this
* Container, if it is found; otherwise, do nothing. If the Valve is
* found and removed, the Valve's <code>setContainer(null)</code> method
* will be called if it implements <code>Contained</code>.
*
* @param valve Valve to be removed
*/
@Override
public void removeValve(Valve valve) {
Valve current;
if(first == valve) {
first = first.getNext();
current = null;
} else {
current = first;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == valve) {
current.setNext(valve.getNext());
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
if (first == basic) first = null;
if (valve instanceof Contained)
((Contained) valve).setContainer(null);
if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
// Stop this valve if necessary
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.valve.stop"), e);
}
}
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.valve.destroy"), e);
}
}
container.fireContainerEvent(Container.REMOVE_VALVE_EVENT, valve);
}
@Override
public Valve getFirst() {
if (first != null) {
return first;
}
return basic;
}
}
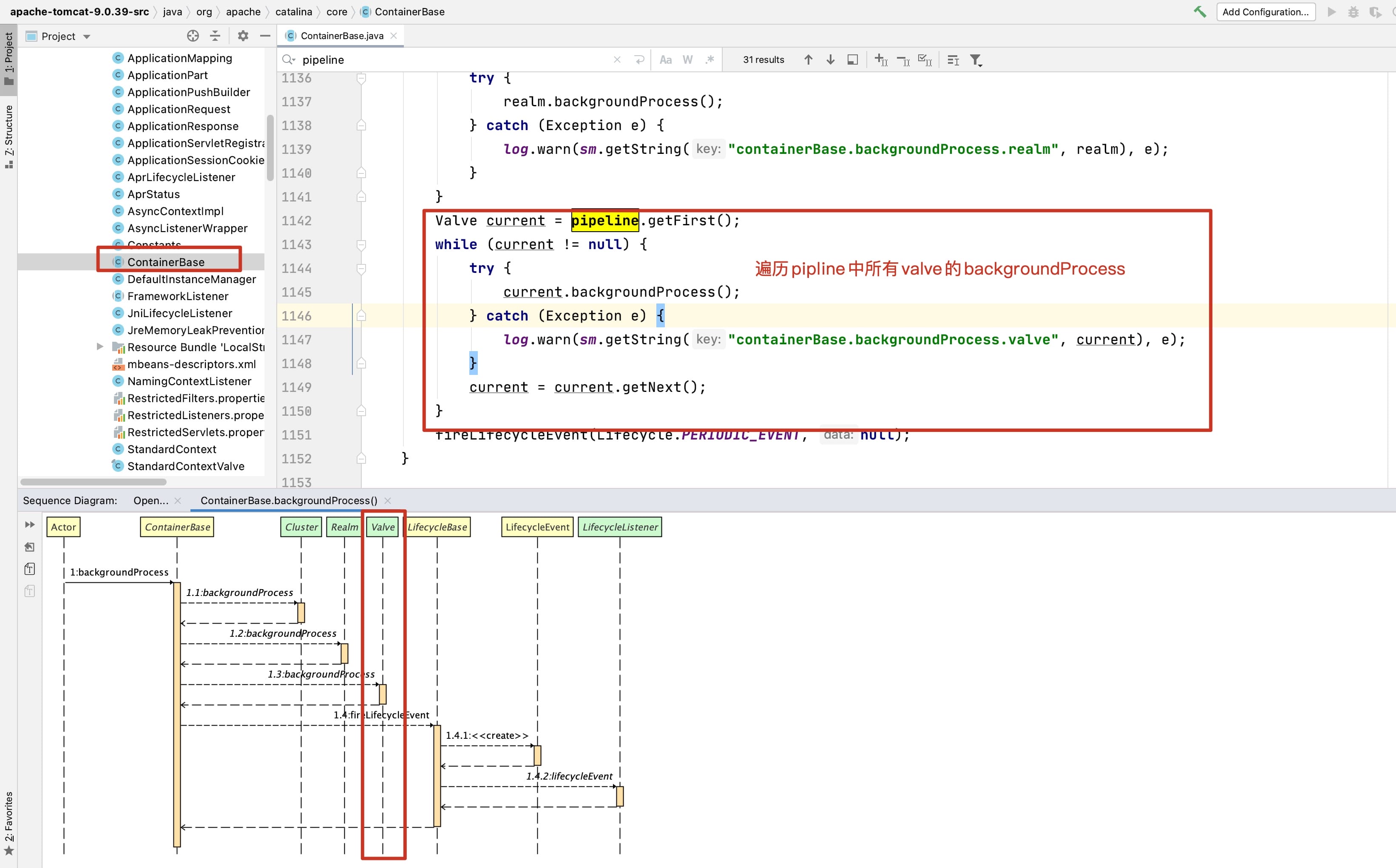
ContainerBase中运用Pipline
那么容器中是如何运用Pipline的呢?
- 容器中是如何运用Pipline的?
由于Container中都有涉及,实现方法肯定是在抽象的实现类中,所以肯定是在ContainerBase中实现。
- 初始化
/**
* The Pipeline object with which this Container is associated.
*/
protected final Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this);
/**
* Return the Pipeline object that manages the Valves associated with
* this Container.
*/
@Override
public Pipeline getPipeline() {
return this.pipeline;
}
- Lifecycle模板方法
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
...
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
...
}
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
...
// Stop the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle &&
((Lifecycle) pipeline).getState().isAvailable()) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).stop();
}
...
}
@Override
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
...
// Stop the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).destroy();
}
...
super.destroyInternal();
}
- 重点是 backgroundProcess方法
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
if (!getState().isAvailable())
return;
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster != null) {
try {
cluster.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.cluster",
cluster), e);
}
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm != null) {
try {
realm.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.realm", realm), e);
}
}
// 看这里
Valve current = pipeline.getFirst();
while (current != null) {
try {
current.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.valve", current), e);
}
current = current.getNext();
}
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT, null);
}
看下相关链路
对比下两种责任链模式
| 管道/阀门 | 过滤器链/过滤器 |
|---|---|
| 管道(Pipeline) | 过滤器链(FilterChain) |
| 阀门(Valve) | 过滤器(Filter) |
| 底层实现为具有头(first)、尾(basic)指针的单向链表 | 底层实现为数组 |
| Valve的核心方法invoke(request,response) | Filter核心方法doFilter(request,response,chain) |
| pipeline.getFirst().invoke(request,response) | filterchain.doFilter(request,response) |
