Tomcat - Service的设计和实现: StandardService
Tomcat - Service的设计和实现: StandardService
提示
上文讲了Server的具体实现了,本文主要讲Service的设计和实现;我们从上文其实已经知道Server中包含多个service了。
- Tomcat - Service的设计和实现: StandardService
- 理解思路
- Service结构设计
- server.xml
- Service中的接口设计
- StandardService的实现
- Engine相关
- Connectors相关
- Executor相关
- Lifecycle相关模板方法
- 补充下MapperListener
- 参考文章
理解思路
- 第一:类比StandardServer, 抓住StandardService整体类依赖结构来理解
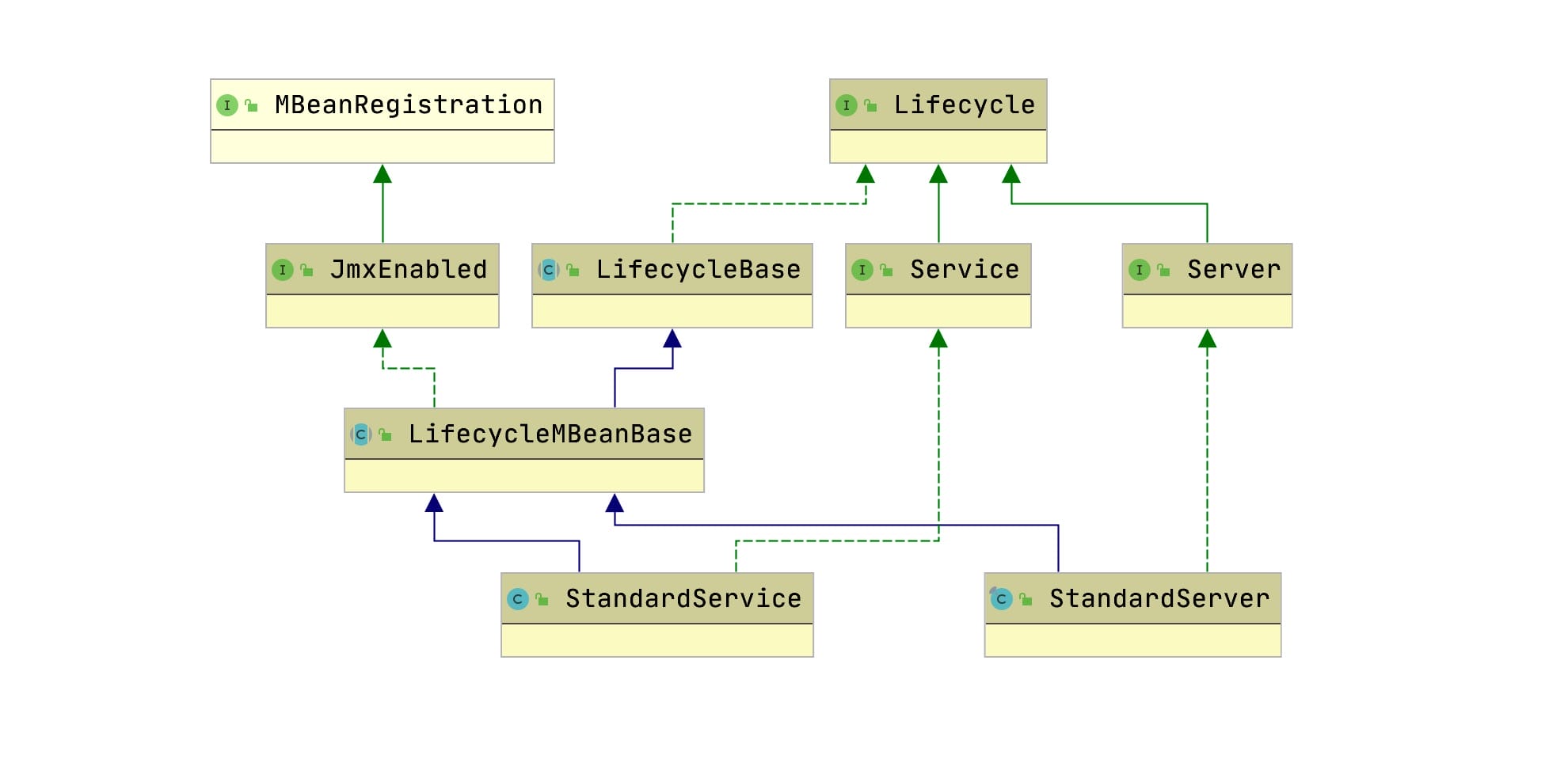
- 第二:结合server.xml中service配置来理解
见下文具体阐述。
- 第三:结合Service Config官方配置文档
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/config/service.html
Service结构设计
我们需要从高一点的维度去理解service的结构设计,而不是多少方法多少代码;这里的理解一定是要结合Server.xml中service配置部分对应理解。
server.xml
- 首先要看下server.xml中Service的配置,这样你便知道了需要了解的4个部分
<!--
每个Service元素只能有一个Engine元素.元素处理在同一个<Service>中所有<Connector>元素接收到的客户请求
-->
<Service name="Catalina">
<!-- 1. 属性说明
name:Service的名称
-->
<!--2. 一个或多个excecutors -->
<!--
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>
-->
<!--
3.Connector元素:
由Connector接口定义.<Connector>元素代表与客户程序实际交互的组件,它负责接收客户请求,以及向客户返回响应结果.
-->
<Connector port="80" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" redirectPort="8443" acceptCount="100"
connectionTimeout="20000" disableUploadTimeout="true" />
<!-- 属性说明
port:服务器连接器的端口号,该连接器将在指定端口侦听来自客户端的请求。
enableLookups:如果为true,则可以通过调用request.getRemoteHost()进行DNS查询来得到远程客户端的实际主机名;
若为false则不进行DNS查询,而是返回其ip地址。
redirectPort:服务器正在处理http请求时收到了一个SSL传输请求后重定向的端口号。
acceptCount:当所有可以使用的处理请求的线程都被用光时,可以放到处理队列中的请求数,超过这个数的请求将不予处理,而返回Connection refused错误。
connectionTimeout:等待超时的时间数(以毫秒为单位)。
maxThreads:设定在监听端口的线程的最大数目,这个值也决定了服务器可以同时响应客户请求的最大数目.默认值为200。
protocol:必须设定为AJP/1.3协议。
address:如果服务器有两个以上IP地址,该属性可以设定端口监听的IP地址,默认情况下,端口会监听服务器上所有IP地址。
minProcessors:服务器启动时创建的处理请求的线程数,每个请求由一个线程负责。
maxProcessors:最多可以创建的处理请求的线程数。
minSpareThreads:最小备用线程 。
maxSpareThreads:最大备用线程。
debug:日志等级。
disableUploadTimeout:禁用上传超时,主要用于大数据上传时。
-->
<Connector port="8009" enableLookups="false" redirectPort="8443" protocol="AJP/1.3" />
<!-- 负责和其他HTTP服务器建立连接。在把Tomcat与其他HTTP服务器集成时就需要用到这个连接器。 -->
<!--
4. Engine
-->
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
</Engine>
</Service>
Service中的接口设计
- 公共属性 , name等
/**
* @return the name of this Service.
*/
public String getName();
/**
* Set the name of this Service.
*
* @param name The new service name
*/
public void setName(String name);
- 父Server相关
/**
* @return the <code>Server</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*/
public Server getServer();
/**
* Set the <code>Server</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*
* @param server The server that owns this Service
*/
public void setServer(Server server);
/**
* @return the parent class loader for this component. If not set, return
* {@link #getServer()} {@link Server#getParentClassLoader()}. If no server
* has been set, return the system class loader.
*/
public ClassLoader getParentClassLoader();
/**
* Set the parent class loader for this service.
*
* @param parent The new parent class loader
*/
public void setParentClassLoader(ClassLoader parent);
/**
* @return the domain under which this container will be / has been
* registered.
*/
public String getDomain();
- Connector相关
/**
* Add a new Connector to the set of defined Connectors, and associate it
* with this Service's Container.
*
* @param connector The Connector to be added
*/
public void addConnector(Connector connector);
/**
* Find and return the set of Connectors associated with this Service.
*
* @return the set of associated Connectors
*/
public Connector[] findConnectors();
/**
* Remove the specified Connector from the set associated from this
* Service. The removed Connector will also be disassociated from our
* Container.
*
* @param connector The Connector to be removed
*/
public void removeConnector(Connector connector);
- Engine
/**
* @return the <code>Engine</code> that handles requests for all
* <code>Connectors</code> associated with this Service.
*/
public Engine getContainer();
/**
* Set the <code>Engine</code> that handles requests for all
* <code>Connectors</code> associated with this Service.
*
* @param engine The new Engine
*/
public void setContainer(Engine engine);
- Excutor相关
/**
* Adds a named executor to the service
* @param ex Executor
*/
public void addExecutor(Executor ex);
/**
* Retrieves all executors
* @return Executor[]
*/
public Executor[] findExecutors();
/**
* Retrieves executor by name, null if not found
* @param name String
* @return Executor
*/
public Executor getExecutor(String name);
/**
* Removes an executor from the service
* @param ex Executor
*/
public void removeExecutor(Executor ex);
StandardService的实现
属性和父Server相关比较简单,这里主要看下其它的方法:
Engine相关
private Engine engine = null;
@Override
public Engine getContainer() {
return engine;
}
@Override
public void setContainer(Engine engine) {
Engine oldEngine = this.engine;
if (oldEngine != null) {
oldEngine.setService(null);
}
this.engine = engine;
if (this.engine != null) {
this.engine.setService(this);
}
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
if (this.engine != null) {
try {
this.engine.start(); // 启动Engine
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.engine.startFailed"), e);
}
}
// 重启Mapper - Restart MapperListener to pick up new engine.
try {
mapperListener.stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.mapperListener.stopFailed"), e);
}
try {
mapperListener.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.mapperListener.startFailed"), e);
}
if (oldEngine != null) {
try {
oldEngine.stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.engine.stopFailed"), e);
}
}
}
// 触发container属性变更事件
support.firePropertyChange("container", oldEngine, this.engine);
}
Connectors相关
/**
* The set of Connectors associated with this Service.
*/
protected Connector connectors[] = new Connector[0];
private final Object connectorsLock = new Object();
/**
* Add a new Connector to the set of defined Connectors, and associate it
* with this Service's Container.
*
* @param connector The Connector to be added
*/
@Override
public void addConnector(Connector connector) {
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
connector.setService(this);
Connector results[] = new Connector[connectors.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(connectors, 0, results, 0, connectors.length);
results[connectors.length] = connector;
connectors = results;
}
try {
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
connector.start();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
sm.getString("standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e);
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("connector", null, connector);
}
public ObjectName[] getConnectorNames() {
ObjectName results[] = new ObjectName[connectors.length];
for (int i=0; i<results.length; i++) {
results[i] = connectors[i].getObjectName();
}
return results;
}
/**
* 当前Service相关的所有Connectors.
*/
@Override
public Connector[] findConnectors() {
return connectors;
}
/**
* 删除connector
*
* @param connector The Connector to be removed
*/
@Override
public void removeConnector(Connector connector) {
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
// 找到conector位置
int j = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < connectors.length; i++) {
if (connector == connectors[i]) {
j = i;
break;
}
}
if (j < 0)
return;
if (connectors[j].getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
connectors[j].stop(); // 停止
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.stopFailed",
connectors[j]), e);
}
}
connector.setService(null); // 去除父service绑定
int k = 0;
Connector results[] = new Connector[connectors.length - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < connectors.length; i++) {
if (i != j)
results[k++] = connectors[i]; // 后续connector向前移位
}
connectors = results;
// 触发connector属性变更事件
support.firePropertyChange("connector", connector, null);
}
}
Executor相关
CRUD方法,代码比较简单
/**
* Adds a named executor to the service
* @param ex Executor
*/
@Override
public void addExecutor(Executor ex) {
synchronized (executors) {
if (!executors.contains(ex)) {
executors.add(ex);
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
ex.start(); // 启动
} catch (LifecycleException x) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.executor.start"), x);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* Retrieves all executors
* @return Executor[]
*/
@Override
public Executor[] findExecutors() {
synchronized (executors) {
Executor[] arr = new Executor[executors.size()];
executors.toArray(arr);
return arr;
}
}
/**
* Retrieves executor by name, null if not found
* @param executorName String
* @return Executor
*/
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(String executorName) {
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
if (executorName.equals(executor.getName()))
return executor;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Removes an executor from the service
* @param ex Executor
*/
@Override
public void removeExecutor(Executor ex) {
synchronized (executors) {
if ( executors.remove(ex) && getState().isAvailable() ) {
try {
ex.stop(); // 停止
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.executor.stop"), e);
}
}
}
}
Lifecycle相关模板方法
首先看 initInternal 方法
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors
* to bind to restricted ports under Unix operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (engine != null) {
engine.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
executor.init();
}
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
// Initialize our defined Connectors
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
connector.init();
}
}
}
initInternal 代码很短,思路也很清晰,就是依次调用了这个成员变量的 init 方法
engine.init()
executor.init
mapperListener.init()
connector.init()
startInternal 方法
/**
* Start nested components ({@link Executor}s, {@link Connector}s and
* {@link Container}s) and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
}
}
}
startInternal 跟 initInternal 方法一样,也是依次调用
engine.start();
executor.start();
mapperListener.start();
connector.start();
补充下MapperListener
mapperListener 的作用是在 start 的时候将容器类对象注册到 Mapper 对象中。
/**
* Create mapper listener.
*
* @param service The service this listener is associated with
*/
public MapperListener(Service service) {
this.service = service;
this.mapper = service.getMapper();
}
service.getMapper() 返回的是 StandardService 对象的 mapper 成员变量。
/**
* Mapper.
*/
protected final Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
Mapper是 Tomcat 处理 Http 请求时非常重要的组件。Tomcat 使用 Mapper 来处理一个 Request 到 Host、Context 的映射关系,从而决定使用哪个 Service 来处理请求。
MapperListener 也是继承自 LifecycleMBeanBase,不过没有重载 initInternal 方法。
- startInternal 方法
@Override
public void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
Engine engine = service.getContainer();
if (engine == null) {
return;
}
findDefaultHost();
addListeners(engine);
Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren();
for (Container conHost : conHosts) {
Host host = (Host) conHost;
if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) {
// Registering the host will register the context and wrappers
registerHost(host);
}
}
}
- findDefaultHost() 方法
首先看 findDefaultHost() 方法
private void findDefaultHost() {
Engine engine = service.getContainer();
String defaultHost = engine.getDefaultHost();
boolean found = false;
if (defaultHost != null && defaultHost.length() > 0) {
Container[] containers = engine.findChildren();
for (Container container : containers) {
Host host = (Host) container;
if (defaultHost.equalsIgnoreCase(host.getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
String[] aliases = host.findAliases();
for (String alias : aliases) {
if (defaultHost.equalsIgnoreCase(alias)) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (found) {
mapper.setDefaultHostName(defaultHost);
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("mapperListener.unknownDefaultHost", defaultHost, service));
}
}
findDefaultHost() 是主要是找出 defaultHost ,并调用 mapper.setDefaultHostName(defaultHost); 这个 defaultHost 是 server.xml 的 <Engine> 标签的属性,一般都是 "localHost"。
从上面代码 for 代码块里可以看出,Host 是 Engine 的子 Container。for 语句就是找出一个名字跟 defaultHost 指定的名字相同的 Host 对象。
- addListeners(engine) 方法
/**
* Add this mapper to the container and all child containers
*
* @param container
*/
private void addListeners(Container container) {
container.addContainerListener(this);
container.addLifecycleListener(this);
for (Container child : container.findChildren()) {
addListeners(child);
}
}
这个方法的作用是,将 MapperListener 这个监听器添加到 Engine 及其子容器中
- registerHost 调用 registerHost方法来注册 Engine 的字容器 Host。
/**
* Register host.
*/
private void registerHost(Host host) {
String[] aliases = host.findAliases();
mapper.addHost(host.getName(), aliases, host);
for (Container container : host.findChildren()) {
if (container.getState().isAvailable()) {
registerContext((Context) container);
}
}
// Default host may have changed
findDefaultHost();
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("mapperListener.registerHost",
host.getName(), domain, service));
}
}
registerHost 方法先调用 mapper.addHost,然后调用 registerContext 方法注册 Host 的子容器 Context。mapper.addHost 方法是将 Host 加入的 Mapper 类的的成员变量MappedHost[] hosts 中。
接着看 registerContext 方法
/**
* Register context.
*/
private void registerContext(Context context) {
String contextPath = context.getPath();
if ("/".equals(contextPath)) {
contextPath = "";
}
Host host = (Host)context.getParent();
WebResourceRoot resources = context.getResources();
String[] welcomeFiles = context.findWelcomeFiles();
List<WrapperMappingInfo> wrappers = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container container : context.findChildren()) {
prepareWrapperMappingInfo(context, (Wrapper) container, wrappers);
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("mapperListener.registerWrapper",
container.getName(), contextPath, service));
}
}
mapper.addContextVersion(host.getName(), host, contextPath,
context.getWebappVersion(), context, welcomeFiles, resources,
wrappers);
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("mapperListener.registerContext",
contextPath, service));
}
}
registerContext 里先获取一些对象,比如 WebResourceRoot 对象、WrapperMappingInfo 对象,然后调用 mapper.addContextVersion。
Mapper#addContextVersion 方法比较琐细,就不细讲了。
其主要逻辑是将 Context 对象,以及 Context 的子容器 Wrapper 对象,每一个都分别构建一个对应的 MappedContext 和 MappedWrapper 对象,然后把 MappedContext 和 MappedWrapper 塞进 ContextVersion 对象中,最后把 Context 和 ContextVersion 的对应关系放在 Mapper 对象的一个 Map 里。这里的 MappedContext 和 MappedWrapper 在 Tomcat 处理 Http 请求的时候是比较关键的。
registerHost 最后再更新了一下可能发生改变里的的 defaultHost。
参考文章
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000022026318
